What is an IP Address?
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a 32-bit unique identification number that is assigned to each computer in a network. It is divided into 4 parts separated by dots, and each part is assigned 8 bits (1 byte), and the limitation for each part ranges from 0-255. Part of an IP address denotes the network address, and part of the IP address denotes the node address.
Example: 192.168.0.1
Usually, computers in a network are identified by their names, but they are automatically resolved or translated into their IP address. There are different classes of IP addresses.
Class A IP address
The class A IP address has the format network.node.node.node, and the range is 1.0.0.0-255.255.255.255.
Class B IP address
The class B IP address has the format network.network.node.nod,e and the range is 128.0.0.0-191.255.255.255.
Class C IP address
The class C IP address has the format network.network.network.node, and the range is 192.0.0.0-223.255.255.255.
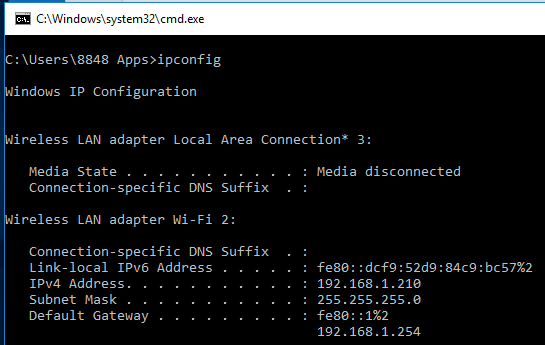
Viewing an IP address
1. Open the command prompt ( Winkey+R type cmd and press Enter )
2. Type “ipconfig” or “ipconfig /all” and press Enter.
The “ipconfig” command shows the IP address, the subnet mask, and the default gateway. The subnet mask hides the network part and the node part of an IP address, and it also shows which class of IP address is being used. The gateway is the computer through which the other computers within a network connect to another network. The “ipconfig /all” command shows all the detailed information about the networked computer.
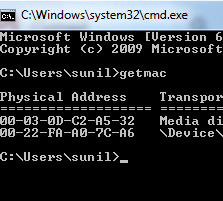
LAN’s Physical Address
Similarly to an IP address, each LAN Card has its own physical address that is unique to it and no other LAN card in the world has the same physical address.
Viewing the LAN’s Physical Address
1. Open the command prompt
2. Type “getmac” and press Enter. The command returns the physical address of the LAN device.
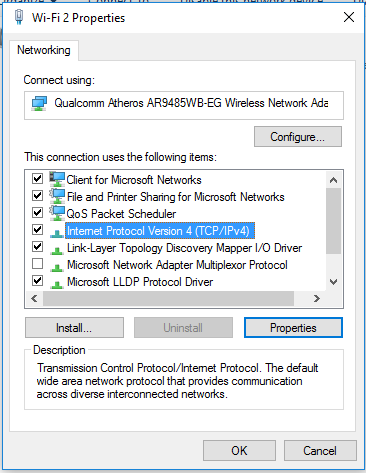
Assigning the IP address
1. To assign the IP address, open the Run command (WinKey + R), type ncpa.cpl, and press Enter
2. In the Local Area Connection Icon, right-click on it and select properties.
3. Select the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click on Properties.
4. We can assign an IP address both automatically and manually. To select an IP address manually, click on the “Use the following IP address” radio button and give your desired IP address and the default gateway. The “Obtain IP address automatically” option assigns an IP address, Subnet mask, and default gateway for a computer in a network automatically.
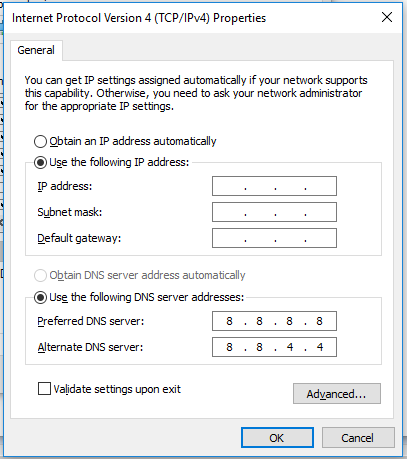
The DNS (Domain Name System) server translates the hostname into the IP address and vice versa. The DNS servers are maintained by the ISP (Internet Service Provider). The DNS server of Google is 8.8.8.8, and the alternate DNS server is 8.8.4.4.
5. Click Ok.
